A Comprehensive Guide to Financial Freedom
In an age where the cost of living is rising, economic uncertainties loom large, and lifestyles are rapidly evolving, the need for effective personal finance planning has never been greater. Whether you earn a modest income or enjoy financial abundance, the ability to plan, manage, and grow your personal finances is a life skill that determines not just your wealth—but your peace of mind.
This article explores the concept of personal finance planning in detail, helping you understand its importance, key components, practical strategies, and common pitfalls to avoid.
What is Personal Finance Planning?
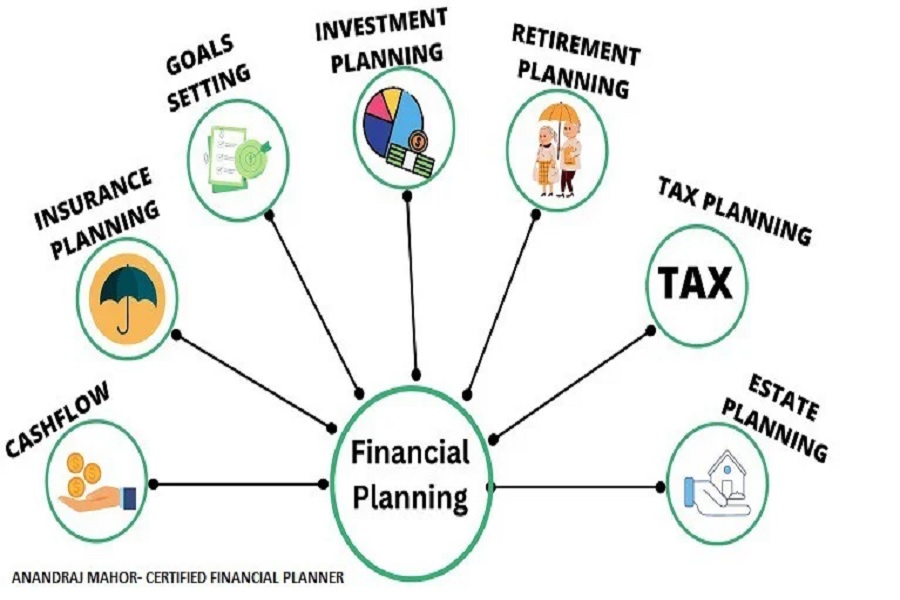
Personal finance planning is the strategic process of managing your income, expenses, savings, investments, insurance, and retirement planning to achieve short-term and long-term financial goals. It’s about making informed decisions with your money — balancing needs, wants, and future aspirations.
Think of it as a roadmap to your financial life — one that helps you stay on course, avoid detours like debt or overspending, and reach your desired destination: financial security and independence.
Why Personal Finance Planning Matters
Achieving Financial Goals: From buying a home or car to funding education or starting a business, structured planning turns dreams into achievable goals.
Reducing Financial Stress: When you know where your money goes and how to prepare for the unexpected, anxiety is replaced by confidence.
Building Wealth: Investing and saving strategically helps grow your wealth over time through compounding and asset appreciation.
Protecting Your Family: Insurance and emergency funds provide a safety net for your loved ones.
Ensuring a Comfortable Retirement: Proper planning means you won’t outlive your savings or depend on others in your old age.
Core Elements of Personal Finance Planning
To build a robust financial plan, you must consider several interconnected areas:
1. Budgeting: Controlling the Flow
A budget is your most powerful financial tool. It tracks your income and expenses, ensuring you don’t spend more than you earn.
Steps to Create a Budget:
List all sources of income (salary, freelance, rental, etc.)
Track all monthly expenses (fixed and variable)
Categorize expenses: Essentials (rent, utilities), non-essentials (entertainment, dining out)
Set limits for each category
Use budgeting tools like Excel, Google Sheets, or apps (e.g., Mint, YNAB)
Tip: Follow the 50/30/20 Rule — 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings/investments.
2. Saving: Pay Yourself First
Saving is not what’s left after spending — it’s what you put aside before anything else. It is the foundation of financial planning.
Types of Savings:
Emergency Fund: Covers 3–6 months of expenses; for job loss or emergencies
Short-term Goals: Vacation, gadgets, car, etc.
Long-term Goals: House down payment, children’s education, etc.
Pro Tip: Automate savings. Set up a standing instruction to transfer a portion of your salary to a separate savings account on payday.
3. Debt Management: Borrow Smartly
Not all debt is bad — but unmanaged debt can cripple your financial freedom.
Types of Debt:
Good Debt: Education loans, home loans (builds assets)
Bad Debt: High-interest loans, credit cards (finances consumption)
Debt Management Strategies:
Pay off high-interest debt first (debt avalanche method)
Consider debt consolidation if managing multiple loans
Avoid minimum payments — it increases total interest paid
Don’t take loans for lifestyle upgrades
4. Investing: Grow Your Wealth
Saving protects your money; investing helps it grow. Smart investments create passive income and beat inflation over time.
Common Investment Options:
Stocks & Mutual Funds: Good for long-term growth
Real Estate: Stable, tangible asset
Fixed Deposits, Bonds: Lower risk, lower return
Retirement Funds (e.g., Provident Fund, Pension Plans): Tax benefits and long-term security
Golden Rule: Don’t invest in what you don’t understand. Diversify across asset classes to manage risk.
5. Insurance Planning: Protect Your Assets
Insurance is your financial safety net. It protects your income, health, assets, and family in case of unexpected events.
Essential Insurance Types:
Life Insurance: Provides financial support to family after your death
Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses
Disability & Accident Insurance: Covers income loss due to disability
Property & Vehicle Insurance: Protects physical assets
Tip: Always read the fine print and understand what your policy covers and excludes.
6. Retirement Planning: Secure Your Future
Retirement planning ensures you can maintain your lifestyle and independence in old age.
Steps to Plan for Retirement:
Estimate future expenses based on lifestyle
Factor in inflation and healthcare costs
Start investing in retirement instruments early (EPF, mutual funds, annuity plans)
Review and adjust your retirement plan annually
Common Mistakes in Personal Finance
Living paycheck to paycheck
Not tracking daily expenses
Ignoring the power of compounding
Delaying saving/investment
Relying solely on credit
Not having health or life insurance
Failing to plan for taxes
Actionable Tips for Financial Success
Start planning today, no matter your age or income
Set SMART financial goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound)
Review your financial plan quarterly
Build a habit of saving, not a reaction to expenses
Educate yourself: Read books like “Rich Dad Poor Dad”, “The Psychology of Money”, or attend online financial literacy courses
Conclusion: Your Financial Journey Begins Now
Personal finance planning is not about being rich — it’s about being prepared, in control, and confident about your future. It empowers you to live life on your terms, make informed decisions, and handle life’s uncertainties with strength.
Start small. Be consistent. And remember — your money should work for you, not the other way around.